Chemical Name:
19-O-beta-glucopyranosyl-13-O-(beta-glucopyranosyl(1-2)-beta-glucopyranosyl(1-3))-beta-glucopyranosyl-13-xhydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acidgalactopyranoside
Characteristics:
- derived from baker’s yeast
- suitable for vegetarian diets
- provided with an Organic ECO Certificate.
Available grades:
- Powder
Applications:
- Dry-mix product
- Weight-losing foods
- Anti-aging foods
- Nutritional & Dietary Products
- Animal nutrition
Certifications:
- BRC
- Kosher/Halal certified
- Non-GMO
- +GMP
- Allergen-free
Saccharomyces boulardii (S. boulardii) is a strain of non-pathogenic yeast first discovered in French Indochina by Henry Boulard in 1920. S. Boulardii has been shown in multiple clinical trials to benefit human health, including reducing the incidence of antibiotic associated and traveler’s diarrhea.Because S. boulardii is a yeast microbe, it cannot be killed by antibiotics and is an ideal supplement to pair with antibiotics. boulardii has been shown to be effective at combating Candida Albicans, H. Pylori, Clostridium Difficile, and other pathogenic yeast and bacteria strains.The highest-quality S. boulardii preparations are lyophilized (freeze-dried) and generally contain 5 billion CFU (colony forming units). Benefits of Saccharomyces Boulardii:
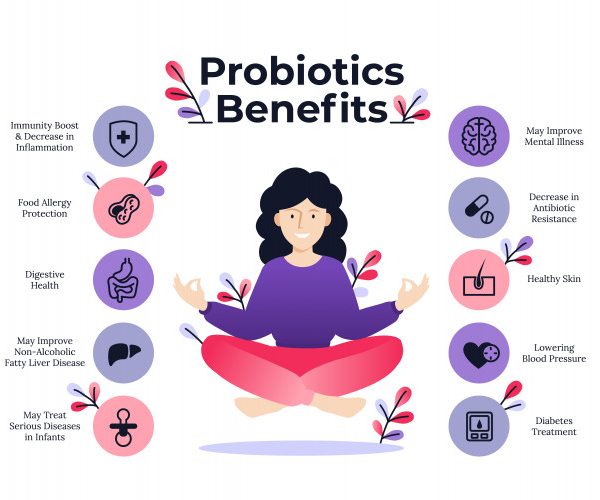
- Saccharomyces boulardii is used in the treatment of a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, anti-biotic-associated diarrhea, nasogastric tube-associated diarrhea, diarrhea in both children and adults, and viral-infection associated diarrhea. It has also shown to weaken the effects of microbial disease caused toxins.
- S. boulardii also has been known to secrete a variety of proteases which have inhibiting abilities on pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- S. boulardii have been found to interact with a variety of microbes within the gastrointestinal tract of the human body and shown inhibitory effects on inflammation causing agents. S. boulardii have been shown to reduce the concentration of diarrhea causing agents and their associated toxins .All types of diarrhea are effectively remedied by S. boulardii including acute diarrhea in adults, children, and infants, chronic diarrhea in AIDS patients (21), and diarrhea caused by bacterial infections.
- S. boulardii has been utilized as a combatant to anti-biotic associated diarrhea, specifically with patients that suffer from Clostridium difficile .C. difficile infection is caused by anti-biotic treatments which eradicate the natural microflora in the lining of the gut causing inflammation to the colon and diarrhea. S. boulardii has been found to replenish a number of microflora in the digestive tract. C. difficile is an anaerobe which produces two toxins (A &B) responsible for nosocomial diarrhea in adults. Studies have found that S. boulardii decreases levels of C. difficile, however the most prominent effect is the reduction in concentration of C. difficile produced toxins, A and B . S. boulardii does so by releasing a 54-kDa protease that proteolytically digests toxin A and B and their brush border membrane receptors. In addition, S. boulardii inhibits C. difficile growth and has the ability to stimulate host mucosal activity to enhance the intestinal mucosal immune response.
- S. boulardii is also effective at inhibiting the effects of Cholera, a condition caused by V. cholerae, a microbe which produces toxins that activate adenylate cyclase to stimulate cyclic AMP production, causing diarrhea. It was found that the mechanism of action involved a secretion of a protease known as 120 kDa which decreases the concentration of cholera-toxin induced cAMP in epithelial cells by inhibiting the stimulation of adenylate cyclase.
- S. boulardii is an effective treatment for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IBD is characterized by the common symptoms of abdominal pain, inflammation of the large intestine, disrupted intestinal transit, constipation or diarrhea, dyspepsia, and distension. Most of these symptoms are a result of an imbalance of microflora. S. boulardii treatment have been found to decrease all the symptoms of IBD.
- S. boulardii decreases the quantity and severity of lesions developed by E. histolylica.
- S. boulardii has been found to be an effective instrument in preventing the relapse of patients with Crohn’s Disease who have already achieved remission. Also, S. boulardii have been found to be advantageous in reducing the gastrointestinal symptoms and diarrhea associated with Ulcerative Collitis.
- S. boulardii has also been shown to fight giardiasis, a condition caused by the bacteria, Giardia lamblia which coats the interior of the small intestine, cutting off nutrient absorption.
- S. boulardii exhibits excellent anti-microbial effects, specifically against the pathogenic bacteria known as E.coli and S. typhi which cause acute infectious diarrhea. The mode of action known as mannose-sensitive adhesion involves the binding of the pathogenic bacteria to specific sites on the surface of S. boulardii by way of lectin receptors. Because of this irreversible adhesion, pathogenic bacteria are kept from invading the brush border, and conveniently excreted.
- Bacterial enteropathogens such as the ones above are responsible for approximately 80% of all cases of Traveler’s Diarrhea (TD). Not only has S. boulardii proved to be an effective remedy for diarrhea, but studies have shown that consumption of S. boulardii as a preventative measure (taken 5-7 days prior to departure) decreases the risk of diarrhea.
- S. boulardii has been found to effectively treat diarrhea associated with viral infections. Among the most studied is chronic diarrhea associated with the HIV virus (AIDS). S. boulardii was given to patients with Stage IV AIDS with the establishment of a control group receiving placebos. Dramatic improvements were seen only 18 months later, including an increase in body weight (whereas the condition of patients given placebos continued to deteriorate significantly) and a decrease of gastrointestinal symptoms.