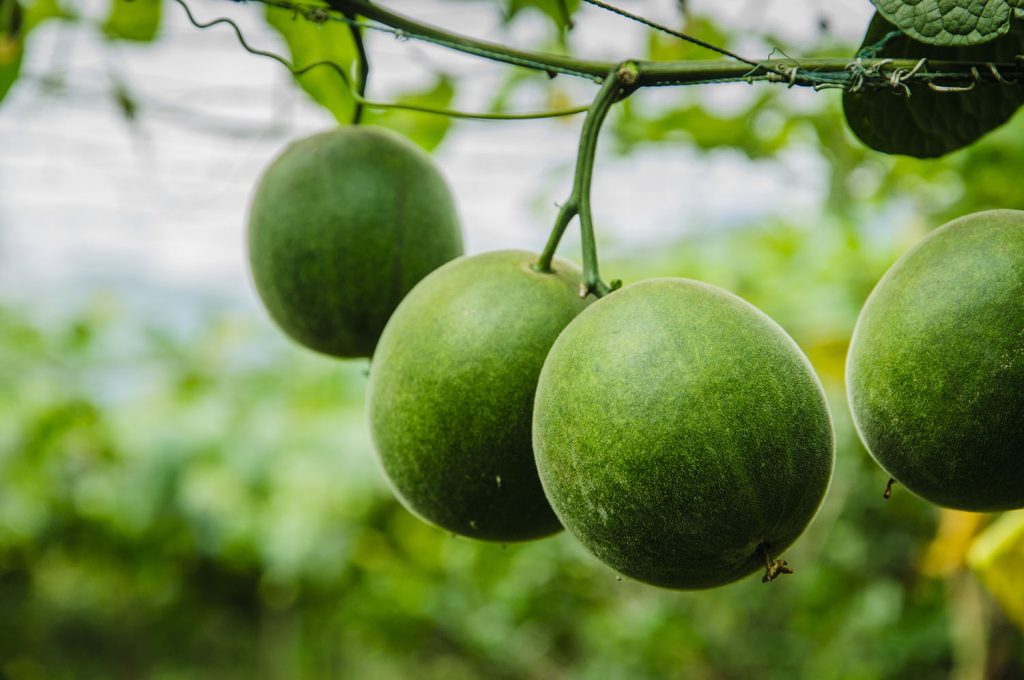

Monk fruit extract
Van Wankum Ingredients is a full service ingredients provider for many different clients in the Food & Beverage, Cosmetics, Pharmaceutical and Health industries. We offer high quality ingredients and additives.
Knowledge of Health & Sports and the accompanying nutrition becomes increasingly sophisticated. Due to the developments in scientific understanding of the influence of nutrition on your health and physical performances, we came to understand that various athletes / sports have different nutritional needs.
Van Wankum Ingredients therefore offers a full range of the latest nutraceutical ingredients for Health & Sports Nutrition, weight-loss and dietary supplements. Underneath you will find our range of natural recources for the Health & Sports Nutrition industry.

Van Wankum Ingredients is a full service ingredients provider for many different clients in the Food & Beverage, Cosmetics, Pharmaceutical and Health industries. We offer high quality ingredients and additives.

Stevia is widely grown for its sweet leaves, which are the source of sweetener products known generically as stevia. The active compounds are various steviol glycosides, which have 250–300 times the sweetness of sugar. It is stable under heat and over a broad range of pH conditions. Stevia is available in different purities from RA60% till RA99%.

Fructo-oligosaccharides are produced from sucrose, through transformation by fructosyltransferases and refinement. It is a probiotic proliferating agent which is not digested and absorbed by the human body and reaches the large intestine directly. Fructo-oligosaccharide has been proved to be the only natural ingredients with both super bifidus factor and water-soluble dietary fiber. It has been approved by governments of more than 200 countries and regions worldwide.

Melatonin is an indoleamine neurohormone whose levels vary in a daily cycle, thereby allowing the entrainment of the circadian rhythms of several biological functions in animals, plants, and microbes. Many biological effects of melatonin are transduced through melatonin receptors, including the MT1, MT2, and MT3 subtypes. Melatonin also acts as a powerful antioxidant that protects lipids, proteins, and DNA against oxidative damage. Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutases, and catalase are upregulated by melatonin, and melatonin scavenges free radicals as a terminal antioxidant.
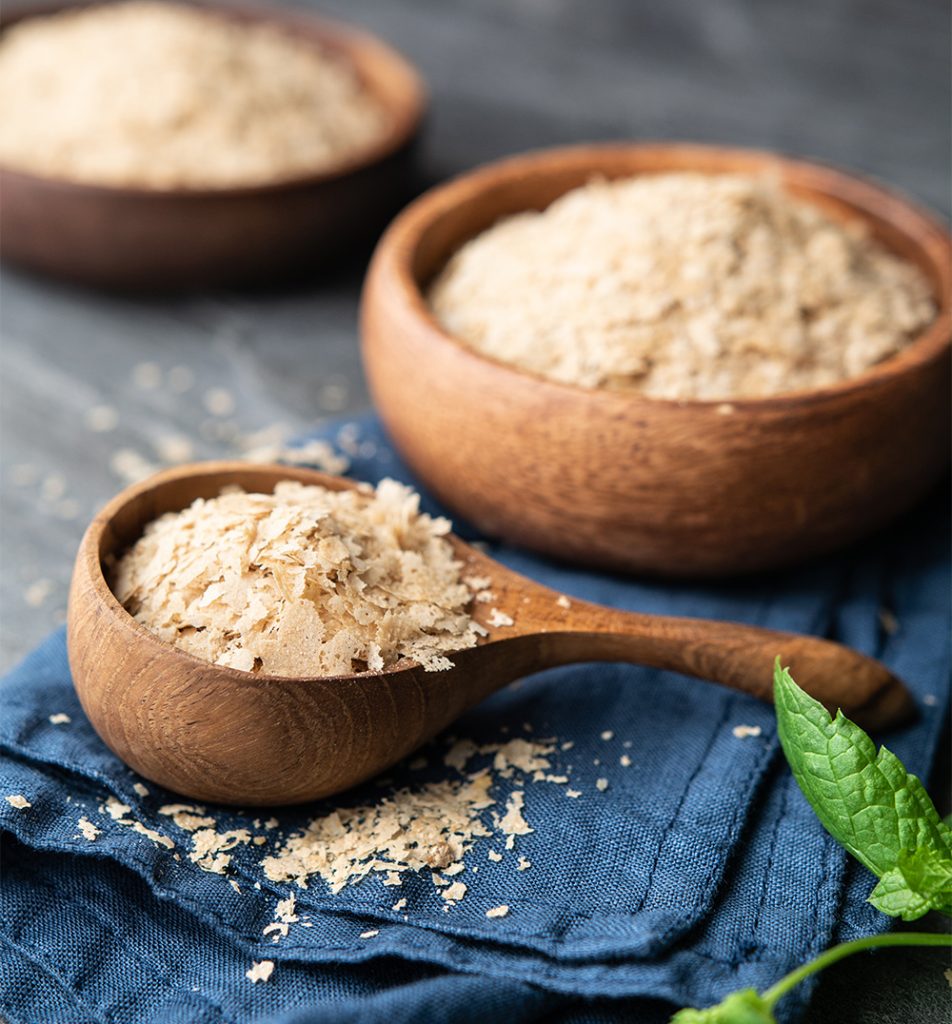

Yeast β-glucan is a scientifically proven biological defense modifier (BDM) that nutritionally potentiates and modulates the immune response. As a supplement, after swallowing orally, Beta glucan is ingested primarily through macrophage and dendritic immune cells, to nutritionally and safely yield, through immune response potentiation and modulation, in many instances various therapeutic healing effects are generated by the immune cells. Yeast beta glucan have been investigated for these immune enhancing properties, particularly their ability to activate macrophage immune cells and NK-Cells, plus in turn, the T-Cells, and B-Cells including selected cytokines and complement cells.
Saccharomyces Boulardii is a kind of unicellular fungi; it belongs to Saccharomyces, a strain of saccharomyces cerevisiae subspecies. As probiotics, S. Boulardii can promote the proliferation and maturity of intestinal epithelial cells, make the villi longer and intestinal crypt deeper, thus to improve the ability of digestion and absorption of nutrients. S. Boulardii can also promote the intestinal mucosa to generate immune globulin (IgA), to build the first line of defense against pathogens.
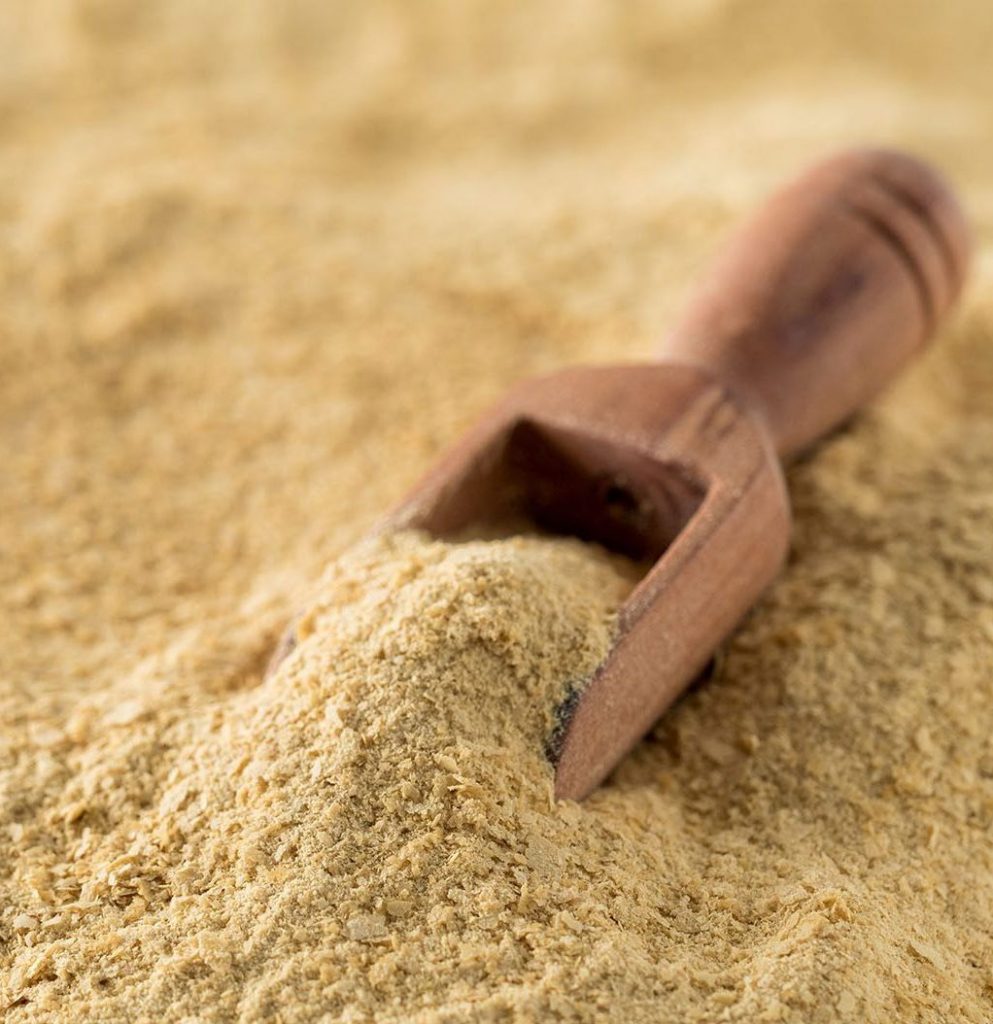

Is an excellent protein source extracted from Baker’s yeast (S.Cerevisiae), with a high protein content between 55% – 70%. With all the essential amino acids for human body and as a new source of non-animal protein, Yeast Protein is a unique substitute of animal protein and soy protein, and it is a true game-changer for the current protein market which is driven by dairy and plant.

Xylo-oligosaccharides (XOS) are polymers of the sugar xylose. XOS is produced from the xylan fraction in plant fiber. Their C5 structure is fundamentally different from other prebiotics, which are based upon C6 sugars. Xylo-oligosaccharides have been commercially available since the 1980s. Xylo-oligosaccharides act as a prebiotic, selectively feeding beneficial bacteria such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli within the digestive tract. A large number of clinical trials have been conducted with XOS, demonstrating a variety of health benefits, including improvements in blood sugars and lipids, digestive health benefits, laxation, and beneficial changes to immune markers.

Sialic Acid also known as N-acetylneuraminic is a key component in Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMO). Contained in breast milk, and is a characteristic functional ingredient. Sialic Acid can effectively promote the development and functional repair of nerve cells, epithelial cells and immune cells, which can get the effect of improving immunity, promoting intellectual development, nourishing skin and anti-aging.

Isomalto-oligosaccharides are a kind of starch sugar made from corn starch by enzymatic
transformation, refining and concentration. It is a widely used functional oligosaccharide because it
can promote the proliferation of Bifidobacterium in human body and it is a water-soluble dietary
fiber with the low calorific value and caries prevention function.
Our services include sampling, economically
and environmentally efficient logistics,
quality documentation and consulting.
These services are provided by a team of
food technologists, commercial, environmental,
logistics and financial experts. Their professional
experience spans the globe. We are committed to
satisfy our customers needs.
© Copyright – VW-Ingredients | Realisation by redefined.